build_embed_linux_system
系统温控驱动管理框架
Linux的Thermal机制是基于Zone为单位的热管理机制,主要由三个部分构成:
- 区域温度检测设备(thermal_zone),用于获取系统温度的设备,包括不限于cpu内部温度检测点,外部温度传感器器件等。
- 区域降温设备(thermal_cooling),提供降温的设备,包含风扇,降频等。
- 温控策略(thermal_governor),管理系统的温控策略,详细可参考内核下的文档:Documentation/admin-guide/pm/cpufreg.rst。
其中thermal_governor从thermal_zone_device获取区域温度,然后根据当前温度,决定调用哪个降温设备来为该区域降温。可以看到thermal的处理即涉及温度采样这类ADC相关的操作,也涉及风扇控制这类PWM相关的操作,因此在理解本节前,建议对掌握之前的知识。
本节将从框架,检测设备,降温设备和控制策略方面描述温控驱动框架;目录如下所示。
thremal_frame
系统温控Thermal框架如下。
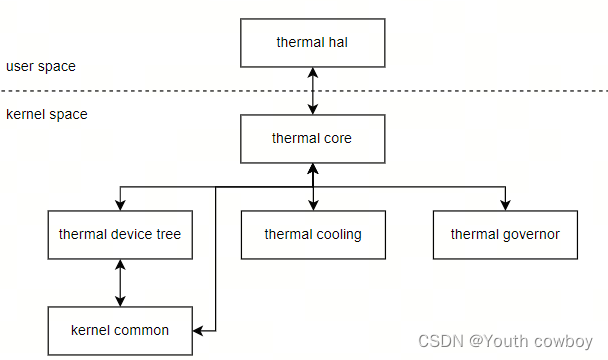
如上图所示, 由如下部分组成。
- Thermal Core: 作为整个框架的核心,负责设备的注册、设备树的解析以及策略的管理等工作。它提供了用户空间的 sysfs 节点,方便用户与系统进行交互。
- Thermal Device Tree: 用于描述系统中的硬件设备,为后续的处理提供资源信息。它根据功能的不同,为 thermal_zone 和 thermal_cooling 设备提供服务。
- Thermal Cooling Device: 代表具体的冷却设备,如风扇、CPU 频率调节器等,负责控制温度。
- Thermal Governor: 根据系统的温度和负载情况,选择合适的冷却设备进行降温,是控制策略的核心。
- Thermal Zone Driver: 作为温度检测设备,负责获取系统的温度信息,如 CPU 内部温度检测点、外部温度传感器等。
其中Thermal core是thermal操作的核心程序,包含模块初始化,组织并管理Thermal Governor、Thermal Cooling、Thermal Driver三个组件,通过sysfs和用户空间交互。
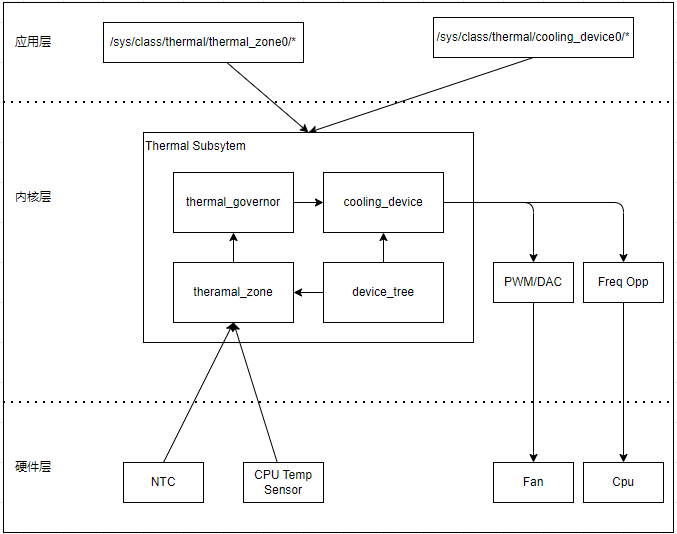
可以看到,Thermal_Zone设备是温控的源头,主要包括采样获取温度信息;然后根据Thermal Governor定义的策略,选择合适的Thermal Cooling Device执行降温的操作,可能包含通过调节PWM加大风扇转速,或者降低CPU频率减少发热等。设备树中则定义了操作的硬件设备和管理的策略,最后在Thermal Core框架的统一管理下共同实现管理策略。
按照这个思路,实现完整的温控框架需要如下流程。
- 温度采样设备驱动实现:可能是芯片内部寄存器,ADC采样的外部NTC器件,或者直接通过i2c/spi接口连接的温度传感器。
- thermal_zone设备抽象与注册:基于温度采样设备硬件,抽象成thermal_zone设备,注册到thermal core框架中。
- 降温设备驱动实现,可能是PWM/DAC控制的风扇,或者CPU主频、电压调节器等。
- thermal_cooling设备抽象与注册:基于降温设备硬件,抽象成thermal_cooling设备,注册到thermal core框架中。
- 控策略实现:根据温度选择合适的降温设备,一般可以选择系统默认支持的控温策略,或者自定义控策略。
整个流程的图形如下所示。
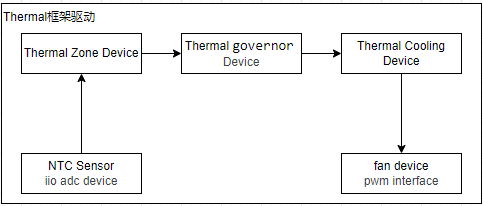
thermal_zone
温度采样设备的驱动主要是ADC,CPU内部温度寄存器或I2C/SPI接口连接的温度sensor;注册到内核后以iio provider的形式可以被其它驱动访问。可以参考前面提到的iio设备驱动框架说明,这里从thermal_zone设备的实现开始说明。
thermal_zone设备是温控系统数据的来源,主要包括采样获取温度信息,通过sysfs接口可以获取到当前的温度,对于此设备主要的接口如下所示。
// 注册thermal_zone设备接口
// @type: 设备类型,生成目录下的type熟悉
// @ntrips: 支持的温度阈值数量
// @mask: 温度阈值掩码,用于确定温度阈值的位数
// @devdata: 设备私有数据
// @ops: 指向 thermal_zone 设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询设备的状态
// @tzp: 指向 thermal_zone 设备参数的指针,包含了设备的一些配置信息。
// @passive_delay: 设备进入被动状态的延迟时间,单位为毫秒
// @polling_delay: 设备轮询获取温度的延迟时间,单位为毫秒
// 返回值: 指向注册的 thermal_zone 设备的指针,如果注册失败则返回 NULL
struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *type, int ntrips, int mask,
void *devdata, struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp, int passive_delay,
int polling_delay)
// 注销thermal_zone设备接口
// @tz: 指向要注销的 thermal_zone 设备的指针
void thermal_zone_device_unregister(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
// 将 thermal_zone 设备和 thermal_cooling 设备进行绑定,同时为该绑定关系设置最大状态值、最小状态值和权重等参数
// @tz: 指向要绑定的 thermal_zone 设备的指针
// @trip_id: 温度阈值的 ID,用于指定要绑定的阈值
// @cdev: 指向要绑定的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针
// @max: 绑定关系的最大状态值,用于限制设备的最大状态
// @min: 绑定关系的最小状态值,用于限制设备的最小状态
// @weight: 绑定关系的权重,用于确定设备在温度阈值触发时的优先级
// 返回值: 0 表示绑定成功,负数表示绑定失败
int thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip_id,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev, unsigned long max,
unsigned long min, int weight);
// 注销thermal_zone和thermal_cooling设备的绑定关系
// @tz: 指向要解绑的 thermal_zone 设备的指针
// @trip_id: 温度阈值的 ID,用于指定要解绑的阈值
// @cdev: 指向要解绑的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针
// 返回值: 0 表示解绑成功,负数表示解绑失败
int thermal_zone_unbind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip_id,
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev);
最关键的数据结构就是thermal_zone_device_ops和thermal_zone_params,这两个数据结构主要用于描述设备的操作和参数,具体如下所示。
// 指定thermal_zone设备执行的操作
struct thermal_zone_device_ops {
// 用于绑定thermal_zone和thermal_cooling设备,如果存在,注册时调用
int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
// 用于解绑thermal_zone和thermal_cooling设备,如果存在,注销时调用(注销和注册需要同时存在)
int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
struct thermal_cooling_device *);
// 获取当前温度的
int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
// 设置温度阈值的
int (*set_trips) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
// 更改设备模式的
int (*change_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,
enum thermal_device_mode);
// 获取指定温度阈值类型
int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trip_type *);
// 获取指定温度阈值的温度
int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
// 获取指定温度阈值的温度
int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
// 获取指定温度阈值的滞后值
int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int *);
// 设置指定温度阈值的滞后值
int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int, int);
// 获取临界温度
int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int *);
// 设置模拟温度
int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int);
// 获取当前温度的趋势
int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,
enum thermal_trend *);
// 当设备温度达到高温状态时调用
void (*hot)(struct thermal_zone_device *);
// 当设备温度达到临界状态时调用
void (*critical)(struct thermal_zone_device *);
};
// thermal_zone设备参数
struct thermal_zone_params {
// 温控策略名称,存储在长度为 THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH 的字符数组中
char governor_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
// 一个布尔值,用于指示是否需要创建从thermal到hwmon的sysfs接口。
bool no_hwmon;
// 热绑定参数(tbp)条目的数量
int num_tbps;
// 指向热绑定参数结构体的指针
struct thermal_bind_params *tbp;
// 此热区域能够以毫瓦(mW)为单位耗散的可持续功率(热量)
u32 sustainable_power;
// 当温度低于(即超调)时,PID 控制器的比例参数
s32 k_po;
// 当温度高于目标值(即超调)时,PID 控制器的比例参数
s32 k_pu;
// PID 控制器的积分参数
s32 k_i;
// PID 控制器的微分参数
s32 k_d;
// 误差不再累积的阈值
s32 integral_cutoff;
// 线性温度调整曲线的斜率。
int slope;
// 线性温度调整曲线的偏移量
int offset;
};
获取的thermal_zone_device则包含热设备需要的所有信息,结构如下。
// 热区域设备结构体
struct thermal_zone_device {
// 热区域设备的唯一标识符
int id;
// 热区域设备的类型,存储在长度为 THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH 的字符数组中
char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
// 表示设备的通用结构体,包含设备的基本信息和操作函数
struct device device;
// 与温度阈值相关的属性组
struct attribute_group trips_attribute_group;
// 指向温度阈值温度属性的指针
struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;
// 指向温度阈值类型属性的指针
struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;
// 指向温度阈值滞后值属性的指针
struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;
// 热区域设备的工作模式
enum thermal_device_mode mode;
// 指向设备特定数据的指针,用于存储与设备相关的私有数据
void *devdata;
// 指向温度阈值结构体数组的指针
struct thermal_trip *trips;
// 温度阈值的数量
int num_trips;
// 用于标记禁用的温度阈值的位图
unsigned long trips_disabled;
// 设备进入被动状态的延迟时间,以时钟节拍为单位
unsigned long passive_delay_jiffies;
// 设备轮询获取温度的延迟时间,以时钟节拍为单位
unsigned long polling_delay_jiffies;
// 当前的温度值
int temperature;
// 上一次记录的温度值
int last_temperature;
// 模拟的温度值
int emul_temperature;
// 设备是否处于被动状态的标志
int passive;
// 上一次触发的低温阈值
int prev_low_trip;
// 上一次触发的高温阈值
int prev_high_trip;
// 一个原子变量,用于标记设备是否需要更新
atomic_t need_update;
// 指向热区域设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询设备的状态
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;
// 指向热区域设备参数的指针,包含了设备的一些配置信息
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
// 指向热区域设备使用的温控策略的指针
struct thermal_governor *governor;
// 指向温控策略特定数据的指针
void *governor_data;
// 用于存储与该热区域设备相关的热实例的链表头
struct list_head thermal_instances;
// 用于分配和管理热区域设备实例 ID 的 ID 分配器
struct ida ida;
// 用于保护热区域设备结构体的互斥锁,防止并发访问冲突
struct mutex lock;
// 用于将该热区域设备结构体链接到其他结构体的链表节点
struct list_head node;
// 用于安排设备轮询工作的延迟工作队列
struct delayed_work poll_queue;
// 热区域设备的通知事件类型
enum thermal_notify_event notify_event;
};
// 定义系统的温控进入不同模式的触发点
enum thermal_trip_type {
THERMAL_TRIP_ACTIVE = 0, // 表示设备处于主动状态
THERMAL_TRIP_PASSIVE, // 表示设备处于被动状态
THERMAL_TRIP_HOT, // 表示设备处于高温状态
THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL, // 表示设备处于临界状态(此时一般会直接触发critical事件)
};
了解了thermal_zone的基本结构和接口,这里以NTC-ADC为例,基于I.MX6ULL和Linux6.1版本来实现的thermal_zone设备驱动,具体流程如下。
zone_dts
首先硬件上连接GPIO1_02,对应ADC1,通道2,这部分可以参考iio章节相关说明:iio子系统相关说明。
pinctrl_adc1: adc1grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO02__GPIO1_IO02 0x400000b0
MX6UL_PAD_GPIO1_IO04__GPIO1_IO04 0x400000b0
>;
};
//加载ADC-iio驱动后,在系统中会添加相应的ADC设备,因为是系统中的唯一iio设备,对应iio:device0
&adc1 {
#io-channel-cells = <1>; //子节点访问时,允许输出的iio channel数目,0表示一路,1表示多路(其它节点使用iio时需要)
io-channel-rangs; //继承了当前节点的子节点可以引用当前节点的 IIO channel
num-channels = <2>; //adc允许的通道数量,驱动访问
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_adc1>; //定义ADC对应引脚的pinctrl配置
pinctrl-name = "default"; //pinctrl配置的别名,default为内核初始化类型
vref-supply = <®ulator_vref_adc>; //基准电压定义,基于regulator获取基准电压
status = "okay"; //模块状态,正常
};
另一部分就是包含系统里thermal_zone设备需要的资源,具体如下。
/ {
// thermal_sensor温控节点
thermal_sensor {
compatible = "rmk,thermal_sensor"; // 与设备树匹配的compatible属性
io-channels = <&adc1 0>; // 对应访问的iio:deviceX中的编号,编号与iio设备的注册顺序有关
polling-delay-passive = <1000>; // 设备进入被动散热状态后轮询读取的延迟时间,单位为毫秒
polling-delay = <8000>; // 设备轮询读取的延迟时间,单位为毫秒
status = "okay"; // 模块的工作状态
// 定义thermal-zone状态应对thermal-cooling的工作状态
// 定义温度阈值和对应的cooling设备,已经cooling设备的工作状态
cooling-map {
active_trip { // active_trip表示设备处于active状态时的阈值
trip,temp = <40000>; // 温度阈值,单位为微摄氏度
cooling-device = <&thermal_fan 1 1>; // 对应cooling设备的路径和状态,在bind时需要(分别对应绑定时的cooling设备,最大值,最小值)
};
passive_trip {
trip,temp = <60000>;
cooling-device = <&thermal_fan 2 2>;
};
hot_trip {
trip,temp = <70000>;
cooling-device = <&thermal_fan 3 3>;
};
crit_trip {
trip,temp = <950000>;
cooling-device = <&thermal_fan 4 4>;
};
};
};
}
在thermal-zone驱动中的解析设备树如下。
static int parse_thermal_dts(struct thermal_sensor_data *data)
{
int ret, index;
int i = 0;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
struct device_node *np = dev->of_node;
struct device_node *cooling_map_np, *trip_np;
struct of_phandle_args cooling_spec;
// 获取被动散热时的轮询延迟时间
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "polling-delay-passive", &data->polling_delay_passive);
if (ret < 0) {
data->polling_delay_passive = THERMAL_SENSOR_PASSIVE_DELAY;
}
// 获取主动散热时的轮询延迟时间
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "polling-delay", &data->polling_delay);
if (ret < 0) {
data->polling_delay = THERMAL_SENSOR_POLLING_DELAY;
}
// 获取iio-channel通道,后续获取温度值时需要
data->chans = devm_iio_channel_get_all(dev);
if (IS_ERR(data->chans)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(data->chans);
if (ret != -EPROBE_DEFER)
dev_err(dev, "Unable to get IIO channels");
return ret;
}
// 解析cooling-map
cooling_map_np = of_find_node_by_name(np, "cooling-map");
if (!cooling_map_np) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to find cooling-map node");
return -ENODEV;
}
data->trip_nums = of_get_child_count(cooling_map_np);
if (data->trip_nums <= 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to find cooling-map node");
return -ENODEV;
}
data->param = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(struct thermal_cooling_trip) * data->trip_nums, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data->param) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to alloc memory");
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 解析cooling-map下的trip,保存信息
index = 0;
for_each_child_of_node(cooling_map_np, trip_np) {
ret = of_property_read_u32(trip_np, "trip,temp", &data->param[index].trip_temperature);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Unable to get trip,temp");
return ret;
}
ret = of_parse_phandle_with_args(trip_np, "cooling-device",
"#cooling-cells", i, &cooling_spec);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Invalid cooling-device entry\n");
return ret;
}
data->param[index].cooling_device = cooling_spec.np;
if (cooling_spec.args_count >= 2) {
data->param[index].min = cooling_spec.args[0];
data->param[index].max = cooling_spec.args[1];
} else {
dev_err(dev, "wrong reference to cooling device, missing limits\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
data->param[index].type = (enum thermal_trip_type)index;
data->param[index].trip_id = index;
index++;
}
of_node_put(cooling_map_np);
dev_info(dev, "parse_thermal_dts success!\n");
return 0;
}
register_thermal_zone
注册thermal_zone设备的主要流程包含。
- 匹配设备树节点,调用probe函数
- 解析设备树,设置thermal_zone配置参数
- 向系统中注册thermal_zone设备
- 使能thermal_zone设备
static struct thermal_zone_device_ops tm_sensor_ops = {
.bind = tm_sensor_bind, // 绑定thermal zone和cooling device时调用(thermal_zone和thermal_cool注册时都会调用)
.unbind = tm_sensor_unbind, // 解绑thermal zone和cooling device时调用
.get_temp = tm_sensor_get_temp, // 获取当前温度,这里是获取ADC采样的温度
.get_trip_type = tm_sensor_get_trip_type, // 获取指定温度阈值类型
.get_trip_temp = tm_sensor_get_trip_temp, // 获取指定温度阈值的温度
.get_crit_temp = tm_sensor_get_crit_temp, // 获取临界温度
.set_trip_temp = tm_sensor_set_trip_temp, // 设置指定温度阈值的温度
};
static int thermal_sensor_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret;
int i, mask = 0;
struct thermal_sensor_data *data;
data = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(struct thermal_sensor_data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "Failed to allocate memory\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
data->dev = &pdev->dev;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, data);
// 解析设备树,获取相关属性
ret = parse_thermal_dts(data);
if (ret != 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "parse dts failed:%d\n", ret);
return -ENODEV;
}
for (i = 0; i < data->trip_nums ; i++)
mask |= 1 << i;
// 向系统中注册thermal zone设备
data->tz = thermal_zone_device_register("thermal_sensor",
data->trip_nums,
mask,
data,
&tm_sensor_ops, NULL,
data->polling_delay_passive,
data->polling_delay);
if (IS_ERR(data->tz)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(data->tz);
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"failed to register thermal zone device %d\n", ret);
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 使能thermal zone设备
ret = thermal_zone_device_enable(data->tz);
if (ret) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev,
"failed to enable thermal zone device %d\n", ret);
goto thermal_zone_unregister;
}
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "thermal sensor probe success\n");
return 0;
thermal_zone_unregister:
thermal_zone_device_unregister(data->tz);
return 0;
}
static int thermal_sensor_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct thermal_sensor_data *data = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
// 注销thermal zone设备
thermal_zone_device_disable(data->tz);
thermal_zone_device_unregister(data->tz);
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "thermal sensor remove success\n");
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id thermal_sensor_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "rmk,thermal_sensor", },
{ }
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, thermal_sensor_of_match);
static struct platform_driver thermal_sensor_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "thermal_sensor",
.of_match_table = thermal_sensor_of_match,
},
.probe = thermal_sensor_probe,
.remove = thermal_sensor_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(thermal_sensor_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("zc <1107473010@qq.com>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("thermal sensor driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
上述就是thermal_zone驱动实现的整体框架,不过有两个函数值得单独讲解, 一个是bind函数,另一个是get_temp函数。
// 绑定thermal zone和cooling device时调用
// 上面提到过,在注册thermal zone/thermal cooling设备时,会调用ops->bind函数
// 其原理是内核中分别维护了thermal zone和thermal cooling的链表,注册时会循环检测链表
// 执行对应绑定
static int tm_sensor_bind(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
struct thermal_sensor_data *data = (struct thermal_sensor_data *)tz->devdata;
struct thermal_cooling_trip *trip = data->param;
for (int index=0; index<data->trip_nums; index++) {
if (trip[index].cooling_device == cdev->np) { //根据设备树,限定只绑定指定的cooling设备
int ret;
ret = thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(tz, //thermal zone设备
trip[index].trip_id, //trip_id,这里是thermal_trip_type
cdev, //cooling设备
trip[index].max, //cooling设备的最大状态(cooling-level指定的档位)
trip[index].min, //cooling设备的最小状态(cooling-level指定的档位)
THERMAL_WEIGHT_DEFAULT);
if(ret) {
dev_err(&tz->device, "binding zone %s with cdev %s failed:%d\n",
tz->type, cdev->type, ret);
return ret;
}
dev_info(&tz->device, "bind device %s with cdev %s\n", tz->type, cdev->type);
}
}
return 0;
}
// 获取当前温度,这里是获取ADC采样的温度
static int tm_sensor_get_temp(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int *temp)
{
int ret, val;
int temperature;
struct thermal_sensor_data *data = (struct thermal_sensor_data *)tz->devdata;
// 从iio接口读取原始的ADC数据
ret = iio_read_channel_raw(&data->chans[0], &val);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&tz->device, "Unable to read temperature:%d\n", ret);
return ret;
}
// 转换为实际的温度值
if (val < 0) {
temperature = 0;
} else {
temperature = (4096 - val) * 110000 / 4096;
}
dev_info(&tz->device, "get temp:%d\n", temperature);
*temp = temperature;
return 0;
}
关于thermal_zone的详细代码见: thermal_zone驱动文件。
cooling_device
风扇设备一般通过PWM或者DAC控制电压来控制转速,这里使用PWM接口控制,对应的驱动实现参考: PWM子系统设备框架。下面进行thermal_cooling设备的说明。
thermal cooling设备作为受控设备,相对于thermal_zone设备会简单些,另外thermal_cooling设备也作为pwm consumer,来访问pwm接口操作实际硬件。关于thermal cooling设备注册访问相关的接口如下所示。
// 注册thermal_cooling设备接口
// @type: 设备类型,生成thermal_cooling目录下的type内容
// @devdata: 设备私有数据
// @ops: 指向 thermal_cooling 设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询设备的状态
// 返回值: 指向注册的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针,如果注册失败则返回 NULL
struct thermal_cooling_device *thermal_cooling_device_register(const char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
// 带设备节点的注册thermal_cooling设备接口
// @np: 指向设备树节点的指针
// @type: 设备类型,生成thermal_cooling目录下的type内容
// @devdata: 设备私有数据
// @ops: 指向 thermal_cooling 设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询设备的状态
// 返回值: 指向注册的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针,如果注册失败则返回 NULL
struct thermal_cooling_device *
thermal_of_cooling_device_register(struct device_node *np, const char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
// 带设备管理的注册thermal_cooling设备接口(驱动移除时自动注销)
// @dev: 指向设备的指针
// @np: 指向设备树节点的指针
// @type: 设备类型,生成thermal_cooling目录下的type内容
// @devdata: 设备私有数据
// @ops: 指向 thermal_cooling 设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询设备的状态
// 返回值: 指向注册的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针,如果注册失败则返回 NULL
struct thermal_cooling_device *
devm_thermal_of_cooling_device_register(struct device *dev,
struct device_node *np,
char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
// 注销thermal_cooling设备接口
// @cdev: 指向要注销的 thermal_cooling 设备的指针
void thermal_cooling_device_unregister(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
最关键的数据结构就是thermal_cooling_device_ops和thermal_cooling_device,这两个数据结构主要用于描述设备的操作和参数,具体如下所示。
// 定义了对冷却设备的操作函数的指针
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
// 获取冷却设备的最大状态值
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
// 获取冷却设备的当前状态值
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);
// 设置冷却设备的当前状态值
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
// 获取冷却设备请求的功率
int (*get_requested_power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *, u32 *);
// 将状态转换为功率
int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long, u32 *);
// 将功率转换为状态
int (*power2state)(struct thermal_cooling_device *, u32, unsigned long *);
};
// 获取的冷却设备的结构体
struct thermal_cooling_device {
int id; // 冷却设备的唯一标识符
char *type; // 冷却设备的类型,例如 "fan"(风扇)或 "cpufreq"(CPU频率调整)
unsigned long max_state; // 冷却设备的最大状态值
struct device device; // 表示设备的通用结构体,包含设备的基本信息和操作函数
struct device_node *np; // 指向设备树节点的指针,设备树是描述硬件设备的树形数据结构
void *devdata; // 指向设备特定数据的指针,用于存储与设备相关的私有数据
void *stats; // 指向统计数据的指针,用于存储与设备性能或状态相关的统计信息
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops; // 指向冷却设备操作函数的指针,这些函数定义了如何控制和查询冷却设备的状态
bool updated; // 一个标志,表示冷却设备是否需要更新。如果为 `true`,则表示设备不需要更新;如果为 `false`,则表示设备需要更新
struct mutex lock; // 用于保护 `thermal_instances` 列表的互斥锁,防止并发访问冲突
struct list_head thermal_instances; // 用于存储与该冷却设备相关的热实例的链表头
struct list_head node; // 用于将该冷却设备结构体链接到其他结构体的链表节点
};
了解了thermal_cooling设备的基本结构和接口,这里以PWM风扇为例,基于I.MX6ULL和Linux6.1版本来实现的thermal_cooling设备驱动,具体流程如下。
cooling_dts
首先硬件上连接PWM7,这部分可以参考pwm章节相关说明:PWM子系统设备框架。
// 芯片原厂提供pwm7设备树
pinctrl_pwm7: pwm7grp {
fsl,pins = <
MX6UL_PAD_CSI_VSYNC__PWM7_OUT 0x110b0 //指定引脚的复用功能,PWM输出模式
>;
};
pwm7: pwm@20f8000 {
compatible = "fsl,imx6ul-pwm", "fsl,imx27-pwm"; //pwm标签,用于设备树匹配
reg = <0x020f8000 0x4000>; //控制pwm模块的寄存器
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 116 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>; //pwm中断,<中断控制器 中断线号 中断触发电平>
clocks = <&clks IMX6UL_CLK_PWM7>, //pwm时钟,ipg为pwm的时钟源,per为pwm经过分频的时钟
<&clks IMX6UL_CLK_PWM7>;
clock-names = "ipg", "per";
#pwm-cells = <3>; //描述引用pwm后,pwm配置项的个数
status = "disabled"; //pwm状态,关闭
};
// 用户扩展pwm7设备树
&pwm7 {
pinctrl-names = "default"; //指定pinctrl的默认配置名称
pinctrl-0 = <&pinctrl_pwm7>; //指定pinctrl的引脚复用
status = "okay"; //pwm状态,开启
};
另一部分就是包含系统里thermal_cooling设备需要的资源,具体如下。
/ {
// ...
// 定义风扇设备
thermal_fan: pwm-fan {
compatible = "rmk,pwm-fan"; // 与设备树匹配的compatible属性
pwms = <&pwm7 0 10000 0>; // 指定PWM设备,通道,周期,极性
#cooling-cells = <2>; // 指定cooling设备的子节点需要的参数个数(thermal-zone选择thermal_fan时,需要此位确定参数)
cooling-levels = <0 102 170 230 255>; // 风扇转速档位,对应cooling设备的状态(满状态255,占空比位x/255*period)
default-fan-level = <2>; // 默认风扇转速档位
status = "okay"; // 模块的工作状态
};
}
在thermal_cooling驱动中的解析设备树如下。
// 解析设备树节点
static int parse_thermal_dts(struct thermal_fan_data *data)
{
int ret;
int i, level_nums;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
struct device_node *np = dev->of_node;
// 获取pwm设备资源,并获取当前pwm状态
data->pwm = devm_pwm_get(dev, NULL);
if (IS_ERR(data->pwm)) {
dev_err(dev, "Could not get PWM\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
pwm_init_state(data->pwm, &data->pwm_state);
// 获取cooling-levels选项,申请对应资源存储
level_nums = of_property_count_u32_elems(np, "cooling-levels");
if (level_nums < 0) {
dev_err(dev, "Count not get cooling-levels!\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
data->cooling_levels = devm_kzalloc(dev, sizeof(u32) * level_nums, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data->cooling_levels) {
dev_err(dev, "Count not malloc cooling-levels!\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
of_property_read_u32_array(np, "cooling-levels", data->cooling_levels, level_nums);
data->cooling_level_nums = level_nums;
for (i=0; i<level_nums; i++) {
if (data->cooling_levels[i] > MAX_PWM) {
dev_err(dev, "cooling-levels[%d] > MAX_PWM, val:%d!\n", i, data->cooling_levels[i]);
return -EINVAL;
}
}
// 获取default-fan-level选项
ret = of_property_read_u32(np, "default-fan-level", &data->cur_fan_level);
if (ret < 0) {
data->cur_fan_level = 0;
}
if (data->cur_fan_level >= level_nums) {
dev_err(dev, "default-fan-level > cooling-levels:%d!\n", data->cur_fan_level);
return -EINVAL;
}
set_pwm(data, data->cooling_levels[data->cur_fan_level]);
data->max_fan_level = level_nums - 1;
return 0;
}
register_thermal_cooling
注册thermal_cooling设备的主要流程包含。
- 匹配设备树节点,调用probe函数。
- 解析设备树,设置thermal_cooling配置参数。
- 向系统中注册thermal_cooling设备。
static const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops thermal_fan_cooling_ops = {
.get_max_state = thermal_fan_get_max_state, // 获取风扇最大状态
.get_cur_state = thermal_fan_get_cur_state, // 获取风扇当前状态
.set_cur_state = thermal_fan_set_cur_state, // 设置风扇当前状态
};
static int thermal_fan_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int ret;
struct thermal_fan_data *data;
struct device* dev = &pdev->dev;
data = devm_kzalloc(&pdev->dev, sizeof(struct thermal_fan_data), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!data) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "[devm_kzalloc]thermal_fan_data failed !\n");
return -ENOMEM;
}
data->dev = &pdev->dev;
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, data);
// 解析设备树,配置系统参数
ret = parse_thermal_dts(data);
if (ret < 0) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "parse_thermal_dts failed!\n");
return ret;
}
// 向系统中注册thermal_cooling设备
data->cdev = devm_thermal_of_cooling_device_register(dev, dev->of_node,
"thermal_fan", data, &thermal_fan_cooling_ops);
if (IS_ERR(data->cdev)) {
dev_err(dev, "Failed to register pwm-fan as cooling device!\n");
return -ENODEV;
}
dev_info(&pdev->dev, "thermal fan driver init success!\n");
return 0;
}
static int thermal_fan_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct thermal_fan_data *data = platform_get_drvdata(pdev);
struct device *dev = data->dev;
dev_info(dev, "thermal fan remove success!\n");
return 0;
}
//匹配的是根节点的compatible属性
static const struct of_device_id thermal_fan_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "rmk,thermal_fan"},
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
static struct platform_driver thermal_fan_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "thermal_fan",
.of_match_table = thermal_fan_of_match,
},
.probe = thermal_fan_probe,
.remove = thermal_fan_remove,
};
module_platform_driver(thermal_fan_driver);
MODULE_AUTHOR("zc <1107473010@qq.com>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("thermal sensor driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
上述就是thermal_zone驱动实现的整体框架,不过这里就如何操作PWM可以实际讲解下。
// 设置PWM值,这部分是对PWM Consumer的应用
static void set_pwm(struct thermal_fan_data *data, int duty)
{
struct device *dev = data->dev;
if (duty > 0) {
// 根据档位中的值计算根据周期的占空比,配置PWM
data->pwm_state.duty_cycle = (u32)data->pwm_state.period * duty / MAX_PWM;
// 设置PWM的周期和占空比, 并使能
pwm_config(data->pwm, data->pwm_state.period, data->pwm_state.duty_cycle);
pwm_enable(data->pwm);
} else {
pwm_disable(data->pwm);
}
dev_info(dev, "device set pwm:%d, %lld, %lld!\n",
duty, data->pwm_state.period, data->pwm_state.duty_cycle);
}
关于thermal_cooling的详细代码见: thermal_cooling驱动文件。
thermal_loading
这里展示thermal设备加载和执行的完整实现流程如下。
- 向系统注册pwm设备驱动

- 向系统注册thermal_cooling设备驱动
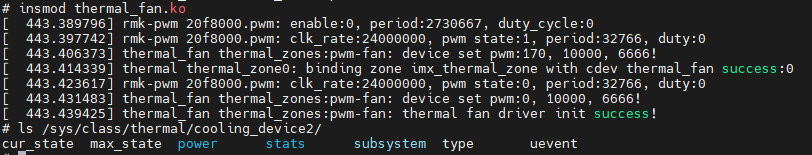
- 向系统注册iio设备驱动
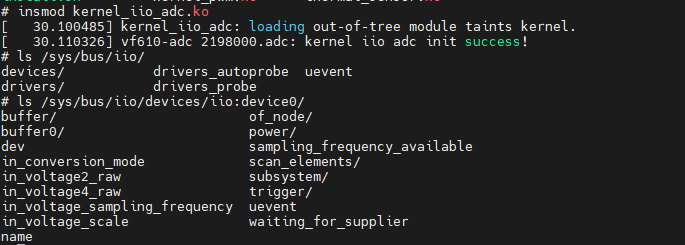
- 向系统注册thermal_zone设备驱动
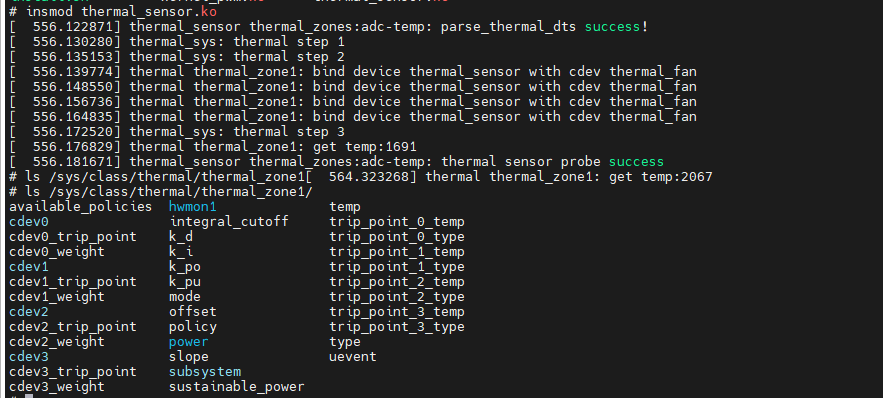
- 当温度变化时,就会操作对应的cooling设备设置,具体如下。
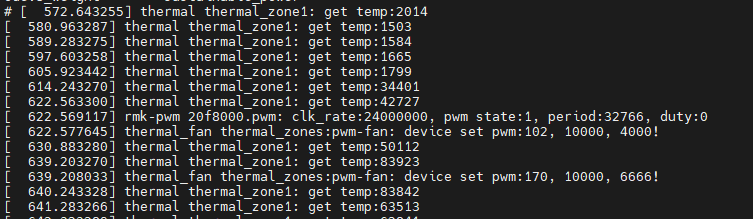
summary
thermal_frame是比较复杂的设备框架,涉及方面广,步骤包含如下所示。
- iio-adc采样
- thermal_zone温控采集管理
- thermal_cooling温控输出
- pwm风扇控制输出
- thermal governor温控方法处理
完整的自己实现thermal驱动可以说十分复杂;在产品开发中很少由用户自己实现,都是使用系统集成的控制方案和温控驱动。例如根据温度控制风扇转速,或者根据温控降低CPU频率。理解了thermal控制,可以更方便的管理芯片的工作频率和工作状态,实现性能和功耗的最佳平衡。
next_chapter
直接开始下一节说明: Watchdog设备管理框架